Among the diseases of the muscle system, osteoarthrosis is a frequency leader.It is believed that at the age of 60, the vast majority of the planet's population have the initial signs of joint cartilage, and 14% are already manifested by osteoarthrosis.The most common version of this disease is osteoarthosis of the knee joints.
Still, "arthrosis" or "arthritis"?
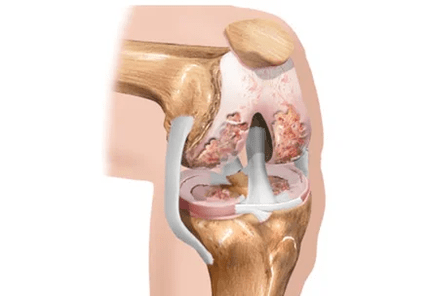
Do not mix these two concepts.Arthrosis is the process of changing the structure of the joints and arthritis is an inflammation that can occur against both the background of the "untouched" structure and the background of arthrosis.
Changes in bones in arthrosis, for example, can be compared to a knotted increase in a tree trunk that increases near the concrete fence and put pressure on this fence with all its weight.
Usually the surface of the bones is separated by two -layer cartilage and meniscus (supplementary cartilage).In addition to the role of the "buffer" between the bones, the cartilage also ensures slippage of bones and mechanical correspondence.Meniscus, which is due to large or small (but frequent) injuries and loses its elasticity, is able to disintegrate completely or partially.
In the presence of age and especially hereditary predisposition, the joint cartilage is thinner.This is the reason why the bones of the hips and lower legs that make up the knee joint at their ends are dangerously approaching each other, and friction may occur.
Usually, as the cartilage thinning, another unpleasant event occurs: the amount of intra -articular fluid decreases.This liquid is not just a purely mechanical "lubrication" of the wrist.It provides nutrition for bones, menisci and joint cartilage.Violation of the "supply" of these structures is a real disaster for the joint!
If the joint is physical overload, bones appear on the surface of the bones and begin to grow, similar to showing or spikes.For the knee joint, such overloads of weights (including the predominance of your own body!), Physical work, knees (such as garden weed), stairs, running, uncomfortable shoes, flat legs and many others.Now it's easy to imagine what happens in the knee joint during joint development and how it appears in the appearance.
How does it work in common?
We have all seen joint cartilage such as chicken bone.This covers small areas of contact in the bones.Underneath the articular cartilage is a subchondral or comprehensive bone.The human muscle bone system is arranged in a similar way.
Most of the person's joints consist of bones, synovial (joint) peel and intra -articular fluid.
What happens to the arthrosis joint?
All the loads already mentioned cause thin bone compression and growth as a result of the increased trauma of the joint cartilage.
The products of the cartridge cartridge formed due to microtrauma fall into the synovial fluid.It is so arranged by nature that alien materials to the synovial shell and provoke its inflammation.The formation of synovial fluid, which is usually a kind of "conveyor belt", is disturbed, similar to a continuous cycle of blood enriching and cleaning.In addition, joint fluid will be less than hyaluronic acid.It's worth telling you about this acid.
Hyaluronic acid provides viscosity of the synovial fluid, creates "buffering" and "lubrication" between the bones, reducing friction against each other.Thanks to this material, the joint fluid in consistency is similar to egg whites rather than water.Another important role in hyaluronic acid is to ensure that nutrients are deep into the articular cartilage, as the nutrition is not available anywhere: the blood vessels are inadequate directly to the cartilage.Similarly, "killed" substances from the cartilage are removed into the joint fluid: using hyaluronic acid molecules.
So there is an increased bone seal and create unbearable conditions for the articular cartilage.
The cartilage signs to adapt to these extreme circumstances and changes in otherwise called transformation.This is primarily decreased by a reduction in cartilage elasticity.
In the late stages of the formation of arthrosis, the bone becomes stiff, but the cartilage is also partially impregnated with calcium.
Symptoms
The development of arthrosis begins with slight pain in the knees, walking on stairs, physical activity, and long walking.Such mild pain can occur for several months or even years.Then they become more shouted.In the early stages of the disease, the knee bones are not deformed, but the mild swelling of the joint itself can be observed.
In the second phase of the disease, the pain becomes more intense and occurs after a slight load.In addition to pain, a crunch appears in the knee joint, which is different from the usual soft abuse of a healthy joint.In addition, the deformation of the joint becomes noticeable, the bones needed for the touch are wider and rough.Wearing the knee at more than 90 degrees becomes problematic.
In the third stage of the disease, the knee pain becomes severe and constant, even in rest periods.Knee mobility will be minimal, often not bending more than 90 degrees and does not spread to the end.The deformation of the joint bones will be so strong that it has a valgus (x-shaped) or the variable (O-shaped) curvature of its legs.
Diagnosis
Control

In the early stages of the disease, the joint does not change, mobile, the muscles around it remain and are strong enough.Only the palpation of certain points (pressure), often on the inner surface of the joint, determining local (local) pain.The doctor asks the patient to perform more squats, bend, straighten his leg in the knee, lift his face on the couch, and lead the bending extensions (called "passive" movements).In this case, you can determine the joint clicks while limiting the amount of pain and movement.With an outstanding inflammatory component, the size of the joint seems to be "pumped" with fluid.By far progress, the knee bending may be partially or completely absent if it is examined, the surface of the joints is uneven, tuber, the limb may be curved (displacement of the limb axis, "recall").
Laboratory and instrumental research
- Mandatory laboratory survey program includesGeneral, biochemical and immunological blood tests, urine analysis- During the general blood test, attention must be paid: the increased levels of leukocytes and the increased proportion of erythrocyte settlement, which indicates inflammation.In the biochemical analysis of blood, metabolic metabolism is important, the level of "liver" enzymes.Immunological analysis determines the presence or deficiency of the signs of systemic inflammation.Urine analysis explores the contents of the "sand" - uric acid crystals.
- Analysis of synovial (joint) fluidIt is prescribed when this liquid is sufficient.That is, when the joint was swollen, swollen.In the conditions of compliance with sterility, the doctor breaks the joint capsule in a strictly defined place, inserts the needle into the joint cavity and then removes excess fluid.Part of the resulting material goes to the laboratory for analysis.At the end of the procedure, anti -inflammatory drugs from the glucocorticosteroid group are most often administered to the joint cavity (such as diprospan).
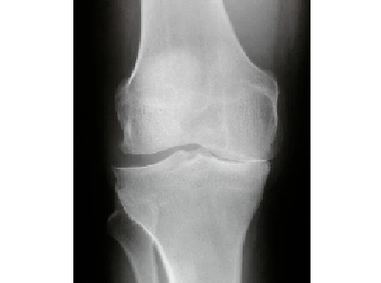 radiography- Both knee joints are required, which is required for the patient's knee and healthy comparison.The picture is used to pay attention to the width of the joint gap (based on the condition of the meniscus and the cartilage), the presence or absence of bone spikes, and the destruction of the bones (destruction).
radiography- Both knee joints are required, which is required for the patient's knee and healthy comparison.The picture is used to pay attention to the width of the joint gap (based on the condition of the meniscus and the cartilage), the presence or absence of bone spikes, and the destruction of the bones (destruction).- Ultrasound of knee jointsResponds to preserving meniscus, Baker cyst, severity of inflammation, presence or absence of uric acid crystals (in the presence of gout).
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)- This study is prescribed if an ultrasound does not give an exhaustive answer to the questions of a specialist.MRI is a must for patients designing arthroscopy.
- Arthroscopy- Allows you to display, that is, to personally evaluate the condition of the joint.The method is essential for contradictory diagnoses, suspected traumatic damage to meniscus and ligaments (you are directly removing the torn meniscus or tapes directly during the examination).
Treatment of the joint joint of the knee joint
The principles of comprehensive treatment must be followed, including the following:
- The patient's detailed awareness of the disease
- Use of physiotherapy exercises that include: special exercises for lying joints, swimming
- To maintain optimal body weight
- Wear orthosis (soft bonding or at least one elastic bandage) during the increased load of the joint - on the road, on a walk and so on.
- No -wheeled methods (physiotherapy).This type of treatment provides excellent results with the arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis).Obviously, this is because the joint is available to influence factors such as magnetic and laser radiation.You can use magnetic currents, UHF, krio-exposure to treat the knee joint (translated from the Greek means the effect of cold).Physiotherapy procedures are widespread, treatment courses are usually short - 10, maximum sessions daily or every other day.Only possible contraindications that include tumors, thyroid and pelvic organs, and systemic (autoimmune) inflammatory diseases.
- Drug treatment.

Principles of osteoarthritis therapy:
- Alleviate the pain
- delay further destruction of joints
- Replace the lost common feature.
Non -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs
For pain relief, NSAID LEE NSAID -no -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs are used.They are used in the form and application of applications (application for the skin).Applications (local therapy) are a very effective method, especially in the early stages of the disease.Before containing a gel or cream containing NSAIDs, you should make sure that the skin has no change, whether rash, pustulas or cracks.The general rule of topical treatment is to use the selected cream or gel at least twice a day, and when discomfort arises - to eliminate the complete disappearance of these manifestations.Intramuscular administration of analgesics is currently not recommended, as the administration of the syringe is not reduced as a result of the risk of side effects, but the opposite.In the case of pronounced inflammation, a large amount of fluid, intraarticular glucocorticosteroid drugs are allowed, but it should be noted that this procedure should be performed at most once every 3 months.
Chondropotectors
A "step" higher than osteoarthritis is an anti -inflammatory effect of chondroitin or glucosamine preparations.They, like NSAIDs, fight inflammation at the level of thin arthritis, but have fewer side effects, and most importantly, they retain the anti -inflammatory effect a few months after deletion.
The Chondroprotectors is a collective name for a group of drugs that are both chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine - cartilage "construction brick".Despite the seemingly high treatment treatment with chondroprotectors, patients' comfort and efficiency are difficult to overestimate.First of all, these accepted substances are perfectly absorbed from the stomach and the loss of drugs is minimal along the "path" to the cartilage.Secondly, they are able to suppress inflammation in the joint and also reliably slow down the process of destroying the articular cartilage!Most often prescribed courses because there is a fairly long "ace" that lasts for several months and sometimes up to six months.
Hyaluronic acid -based drugs are called hyaluronates.These funds are sold in the form of syringes for intraarticular administration.Hyaluronets are artificial synovial fluid.The effect of treatment with this method can take up to 12 months.
Surgery for arthrosis of the knee joint
Like hip joint arthrosis, surgery is also in the case of severe changes and lasting loss of function.In the case of gonarthrosis, two types of interventions are currently performed: artrodesis (motionless compound) and endoprostany.The first operation is rarely performed, according to special indications, when the installation of endoprothesis is impossible for any reason.The result of this operation is that the knee will be motionless.But it doesn't hurt.The endoprosttetic operation is much more profitable for function.Remember that this operation is not performed with high weight - during the postoperative period, the risk of complications is too high.From the moment of removal of damaged sections of the joint and from installation of the prosthesis, until the function is completely renovated, up to three weeks.
How can ridiculous osteoarthrosis be threatened?
Over time, osteoarthrosis does not turn back, but only worsens, especially while maintaining provoking factors.Note the most important sources of health and lifetime of patients with osteoarthritis.
- Chronic pain of different intensity- Very important risk factor, especially in old age.The ever -experienced discomfort can lead to sleep disorders, mood and even reduced background of depression.It is difficult to predict which chain of the side effects pulls the phenomena listed.
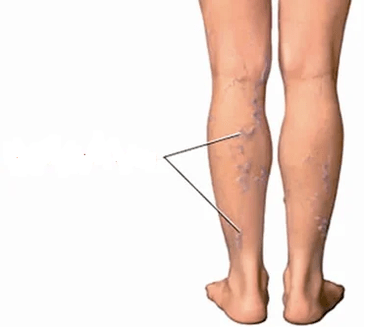
- Veins' pathology- Continuous inflammation of the knee area, an increase in bone spikes and aneophytes that can mechanically damage popliteal vessels and veins of the veins of the legs.Occasionally, orthopedists refuse to function until the varicose nodes are removed, but the flebologists (veins' experts) do not begin surgery in veins until there are changes in the knee joints.
- Reduced limb function- With a far -reaching process, the joint can completely lose its ability to move, and in most cases it is a sign of disability.
- to involve other joints- We have already learned that such a seemingly normal phenomenon, such as flat legs, can pull the knee joint with them and lead to osteoarthrosis.Similarly, along the chain, it is involved in the painful process of the knee joint from the opposite side.If the patient neglects the recommendations, refuses to wear the reed and rather "affect the two", then the arthrosis of the hip joints will soon develop.The legs are twisted, the walk will be a "duck".
- immobility- Such a serious complication of the disease occurs in cases where the bones of the joint are significantly destroyed, there is no cartilage, the movement of the joint is at all painful or impossible due to the fusion of the bones (called "ankylosis").In this situation, only surgery can help the patient, but only if it is technically implemented.Defeat is dangerous in general: obesity, osteoporosis, muscle atrophy, and rapid development of internal organs.In addition, an immobilized person must, of course, constantly take care of it.
- Inexperience- Unfortunately, there are many states that make the operation impossible and one of them is far from "neglected" osteoarthritis in patients over 80 years of age who are involved in severe related illnesses.
Prevention
- Excludes joint injuries.There seems to be nothing easier.For a while leaving jumps, running, walking on the stairs, dance, high heels are not at all difficult.In practice, it turns out that this point causes most protests from patients.A person, if you are recently suffering, is usually not ready for the fact that some important point in your daily life is missing.But if you do not follow these tips, there is a risk that quality of life and disability will be rapidly reduced.
- Weight loss and maintaining optimal borders are an extremely important recommendation!No matter how wonderful it has an effect or device, fat people will not be able to appreciate it.Because while the joints are overweight, the microtraumas are repeated daily.This can reduce all your efforts to "no".In addition, obesity is a direct contraindication for some treatment methods.
- Walk with support.The universal rule of unloading the community is as follows: the reed, crutches or railing must be in the opposite hand of the limb affected.That is, if the right knee hurts, the reed should be kept left and vice versa.
- Correction of flat legs.How do you seem to connect the flat foot and arthrosis of the knee joint?It turned out to be directly.If the foot is not properly fitted (now it is talking about longitudinal or mixed flat legs, not transverse), the load is redistributed in the knee joint.In this case, the severity of the body is one step not in the center of the joint, but on the right or left.Accordingly, the right or left meniscus suffers better, and since it suffers more, we wear it faster.Then comes the joint cartilage "line" where the meniscus cannot cope with its function.This process ends with the typical unilateral "Arthrose" changes in the knee joint (appearance of bones outgrowths).





































